(Picture Source:Sogou)
The orangutan is the only ape in Asia, and is now the only steam-filled jungle in Borneo and Sumatra. In primates, thetwo species of the orangutans are prominent in many ways, the world's largest arboreal, and the slowest _ mammal. The orangutans are very careful when climbing in the tree. Because it is too heavy to jump, the way they go through the canopy gap is to swing back and forth on a tree until another tree can be caught, and they will always grab the branches with two forelegs. This mode of action is through their long arms and shorter legs (30% shorter than the arm) and long hooks Like palms and soles, their arms and legs can move freely in many directions. Orangutans rarely go down to the forest floor, with the exception of adult male Borneo orangutans, who spend up to 5% of their time on the ground. Early orangutans may be more adapted to habitat, but the arboreal lifestyle of existing orangutans proves that they lived on forest roofs for a long time. The red apes have a large chin, wrinkled tips and thick Enamel on their large, flat molars-a perfect anatomical structure that helps tear open woody fruit and branches with termites' nests. Break hard seeds and tear off bark.
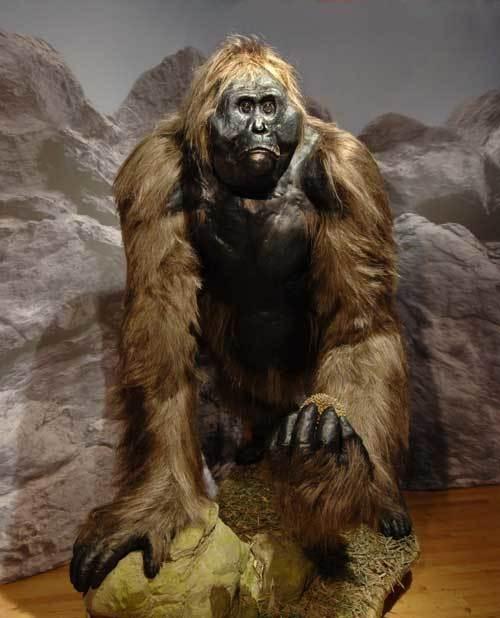

By sequencing the proteins extracted from the enamel 2 million years ago, we can confidently reconstruct the evolutionary relationship between animal species, says Professor EnricoCappellini of the University of Copenhagen. Genetic material, such as ancient proteins and ancient DNA, preserved in fossils tens of thousands or even millions of years ago, records the "code" of early species evolution. The results of the study confirm that giant apes are most closely related to Asian orangutans who now live in Southeast Asia.
Gigantopithecus is one of the largest primates living on Earth. Fossil evidence has been found in southern China, such as Guangxi, Hainan, Guizhou, Chongqing and Hubei, and so far 17 fossil sites have been found, most of them in southwestern Guangxi. Fossil records indicate that the giant apes are the largest apes, standing 3 meters tall and weighing 600 kilograms. This is huge, like apes that orangutans live on the ground, probably the largest ape in the world. His weight is estimated to be more than 200 kilograms, and this primate has huge molars and has The thick enamel layer, the high tooth crown and the short tip. The fossil found in 1935 is a tooth whose volume is about five times the size of the modern people. In 1955, in Guangxi, many have been found, so far, three and nearly thousands of teeth have been found in the mandible. The great ape is an extinct side branch of the ape-type evolution system. The great ape may be the prototype of the diamond, which is similar in shape to the modern apes, and the difference is that their body is much larger. The great ape is the most developed ape in history, with a height of nearly 10 feet and a body weight of more than 1000 pounds. Co-author of the paper, National Museum of Guangxi The proteome was extracted from a fossil of the ape's teeth. The fossil of this tooth is from the air-blown wind tunnel in TianDong County, Guangxi. The wind tunnel is a very high cave to the ground, the hole is about 77 meters from the ground, and the depth of the cave is about 19 meters. In 2008, the study team of the Guangxi National Museum carried out systematic excavation of the cave, and found more than 90 giant ape-tooth fossils. Wang Wei, the author of the paper, said the discovery was to understand the origin, evolution and spread of early human beings and open a window.
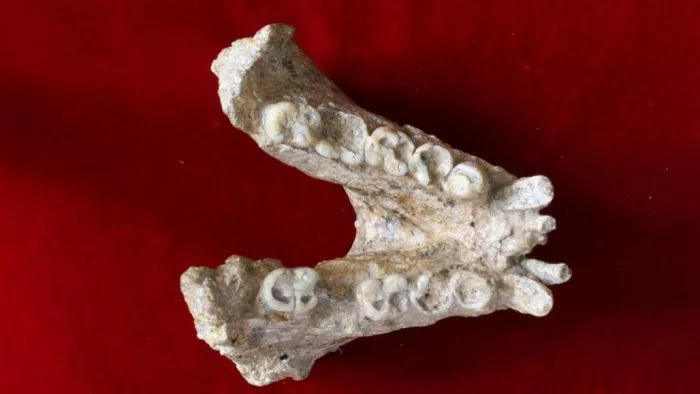

On November 14, Beijing time, the journal Nature, an authoritative academic journal in the world, published a report entitled Enamel Proteome indicating that Giant apes are members of early differentiated orangutans, and published the latest research results. The report was co-authored by 18 scientists from six countries: China, Denmark, France, Spain, Germany and Britain. They successfully extracted genetic information from the enamel of a giant ape tooth fossil found in Guangxi 1.9 million years ago through advanced ancient protein sequencing technology in Copenhagen, Denmark. As a result, scientists rebuilt giant apes and orangutans currently living in southeastern Asia. The evolutionary relationship between them.
On November 15, Guangxi's National Museum of the People's Republic of China introduced 18 scientists from six countries to successfully extract the genetic material from the fossil of the gibbon, Guangxi, and confirmed the close evolutionary relationship between the extinct species and the Asian orangutan. The great apes were isolated from the family of orangutans about 12 million years ago and evolved independently. This is the first time to extract such ancient protein evidence in the fossil of the subtropics.